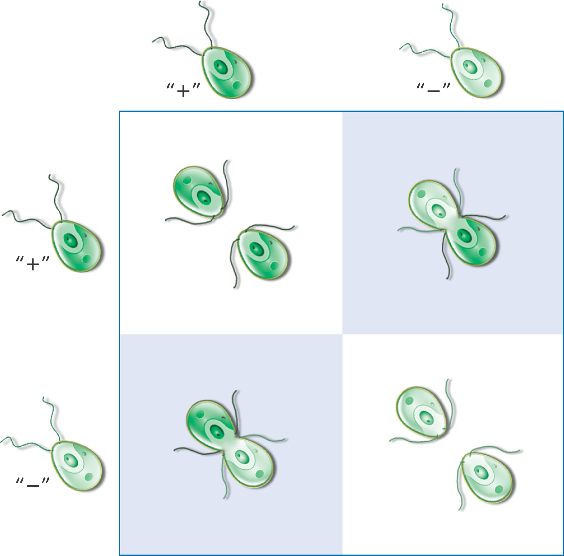
 Chlamydomonas isogametes are haploid and consist of opposite
mating types:
Chlamydomonas isogametes are haploid and consist of opposite
mating types: plus (+) and minus (-).
The isogametes are morphologically and genetically indistinguishable, differing only in surface chemical makeup.
Mating (fertilization) only occurs between + and - cells, which can fuse to form a
diploid zygote.