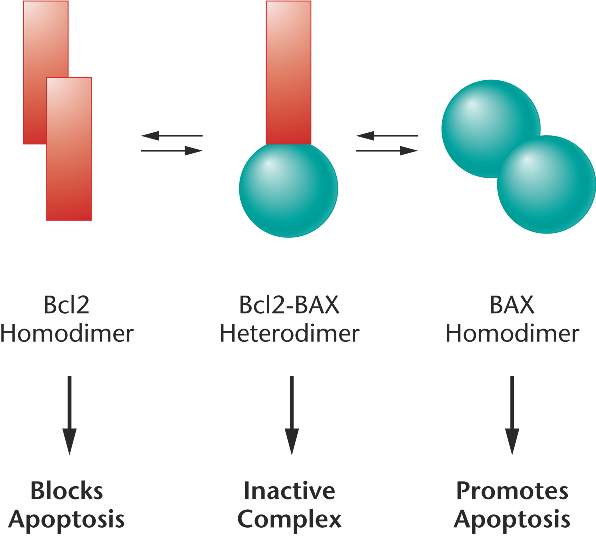
 The relative concentrations of the Bcl2 and BAX proteins regulate
apoptosis.
The relative concentrations of the Bcl2 and BAX proteins regulate
apoptosis.
A normal cell contains a balance of Bcl2 and BAX, which form inactive heterodimers.
The p53 protein induces transcription of BAX and inhibits transcription of Bcl2,
leading to BAX homodimers and apoptosis.
Bcl2 overexpression or defective p53 proteins may prevent
apoptosis and result in cancer.