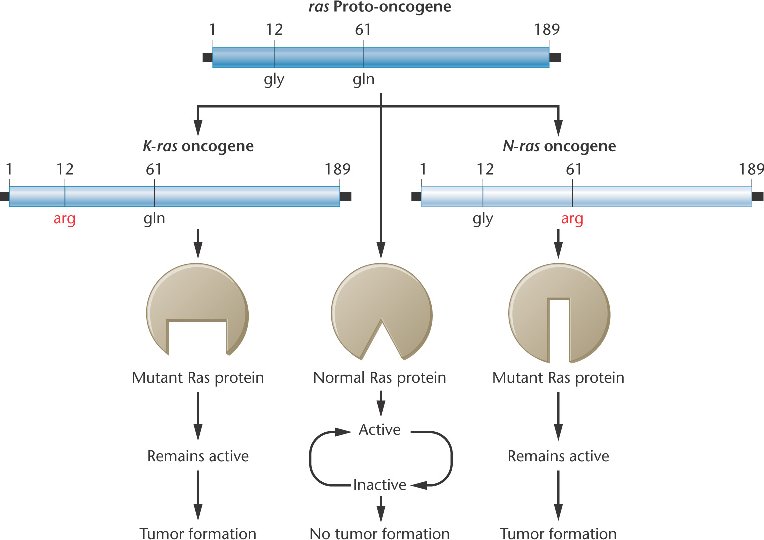
Mutations in
the ras proto-oncogene that substitute arginine for either
GTPase at amino acid 12
or for
glycine at amino acid 61
convert the gene into an oncogene (K-ras and N-ras) by inactivating its GTPase function, thus keeping the protein in a perpetual active state and promoting abnormal cell division.
