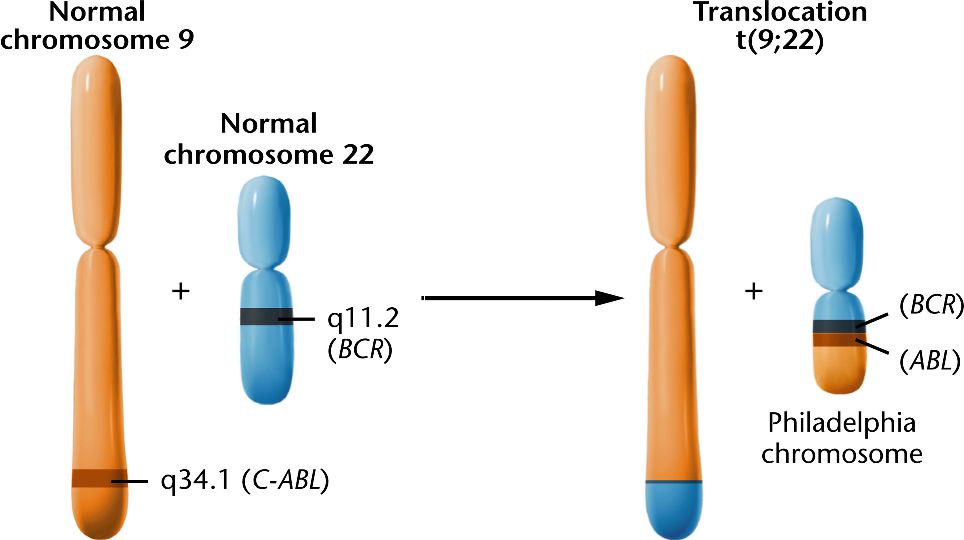
A reciprocal translocation t(9;22) produces the
the Philadelphia chromosome, which
results in the fusion of the C-ABL proto-oncogene on chromosome 9 with the BCR gene on chromosome 22.
The fusion protein allows cells to escape control of the cell cycle,
leading to chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).
